The worksheet on accuracy and precision embarks on an intellectual journey, inviting readers to delve into the fundamental concepts of measurement, accuracy, and precision. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of the factors that influence the reliability of measurements, offering practical strategies to enhance accuracy and precision in various contexts.
Delving deeper, this worksheet unravels the significance of accuracy and precision in scientific research, where reliable measurements are paramount for drawing valid conclusions. It also highlights the implications of inaccurate or imprecise measurements in everyday life, emphasizing the importance of accurate data in decision-making and problem-solving.
Definition and Importance: Worksheet On Accuracy And Precision
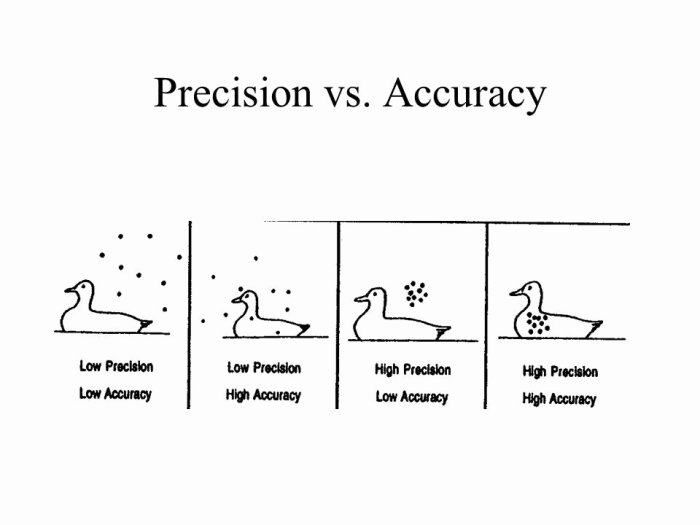
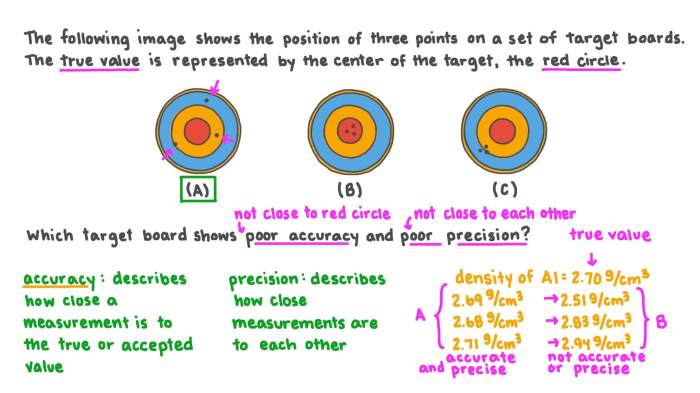
Accuracy and precision are two fundamental concepts in measurement that quantify the closeness of a measurement to the true value and the consistency of repeated measurements, respectively. Accuracy reflects the degree to which a measurement matches the actual value, while precision indicates how closely multiple measurements of the same quantity agree with each other.
Accuracy and precision are crucial in scientific research, where precise and accurate measurements are essential for reliable data analysis and valid conclusions. In everyday life, accuracy and precision are also important, such as in medical diagnostics, engineering, and manufacturing, where precise and accurate measurements ensure safety, quality, and efficiency.
Factors Affecting Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy and precision can be affected by various factors, including:
- Measurement instruments:The quality and calibration of instruments used for measurement can significantly impact accuracy and precision. Poorly calibrated or unreliable instruments can lead to inaccurate or imprecise measurements.
- Environmental conditions:Factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibrations can influence the accuracy and precision of measurements. Changes in these conditions can affect the performance of instruments and the stability of the measured quantity.
- Observer bias:Human error can introduce bias into measurements, affecting their accuracy and precision. Subjective judgments, personal interpretations, or fatigue can lead to variations in measurements.
- Sample size:In statistical measurements, the sample size can affect the precision of the results. Larger sample sizes generally yield more precise estimates of the true population value.
Methods to Improve Accuracy and Precision, Worksheet on accuracy and precision
Several techniques can be employed to improve accuracy and precision in measurements:
- Calibration:Regularly calibrating measurement instruments against known standards ensures their accuracy and reduces systematic errors.
- Environmental control:Maintaining stable environmental conditions during measurements minimizes the impact of external factors on accuracy and precision.
- Multiple measurements:Repeating measurements multiple times and averaging the results can reduce random errors and improve precision.
- Training and standardization:Providing proper training to observers and establishing standardized measurement protocols help minimize observer bias and improve accuracy.
Examples and Applications
Accuracy and precision are crucial in numerous fields, including:
- Scientific research:Precise and accurate measurements are essential for data analysis, hypothesis testing, and drawing valid conclusions.
- Medical diagnostics:Accurate measurements are vital for diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions, ensuring appropriate treatment and patient safety.
- Engineering:Precise measurements are necessary for designing, constructing, and testing engineering structures and systems.
- Manufacturing:Accurate measurements ensure the quality and consistency of manufactured products, reducing defects and improving efficiency.
Inaccurate or imprecise measurements can have serious consequences. For example, in medical diagnostics, inaccurate measurements can lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment, while in engineering, imprecise measurements can result in structural failures or system malfunctions.
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between accuracy and precision?
Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measurement to its true value, while precision refers to the consistency of repeated measurements.
How can I improve the accuracy of my measurements?
Use calibrated instruments, follow standardized procedures, and minimize sources of error.
What are some common factors that affect precision?
Environmental conditions, instrument limitations, and operator variability can all impact precision.