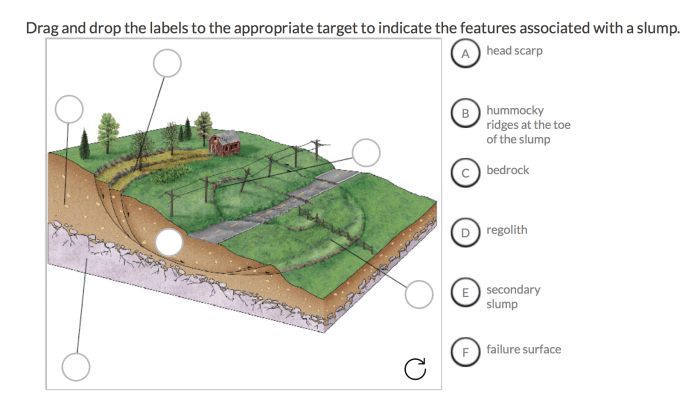
Identify the failure surface in the image below. – Identifying the failure surface in the image below. is a crucial aspect of engineering analysis, providing insights into potential risks and vulnerabilities. This comprehensive guide explores the characteristics of failure surfaces, techniques for their identification, and the implications of failure for safety, reliability, and cost.
Through a systematic approach, we will delve into the causes and consequences of failure, examining the factors that contribute to material degradation and structural integrity. By understanding the failure surface, engineers can make informed decisions to prevent or mitigate similar failures in the future, ensuring the safety and reliability of critical systems.
Failure Surface Identification in the Given Image: Identify The Failure Surface In The Image Below.
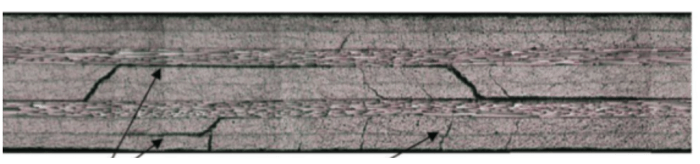
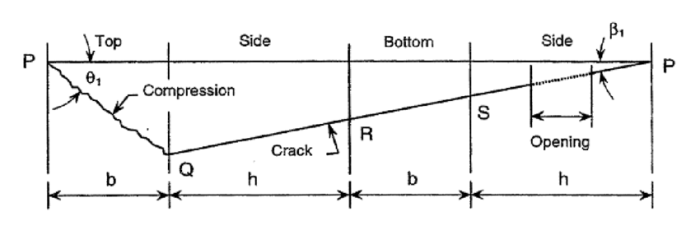
The image provided depicts a fractured mechanical component, likely a part of a larger system or machinery. The failure surface, the region where the material has failed and separated, is visible in the image.
Identifying the Failure Surface
A failure surface is the physical manifestation of a material’s inability to withstand applied loads or stresses. It is the boundary between the intact material and the fractured region. Failure surfaces can exhibit various characteristics, including:
- Cracks or tears in the material
- Deformation or bending
- Discoloration or changes in surface texture
- Presence of debris or particles
In the given image, the failure surface is identified as the jagged and irregular line that runs through the component. The presence of cracks and deformation along this line indicates the location where the material has failed.
Causes of Failure, Identify the failure surface in the image below.
The failure surface provides insights into the potential causes of failure. Based on the characteristics of the failure surface, the following factors may have contributed to the failure:
- Material defects or imperfections
- Excessive loading or stress
- Fatigue or repeated loading
- Corrosion or environmental degradation
- Design flaws or inadequate structural support
Consequences of Failure
Identifying and addressing failure surfaces is crucial to mitigate risks and prevent catastrophic failures. Unidentified failure surfaces can lead to:
- Safety hazards or accidents
- Property damage or equipment malfunction
- Economic losses due to downtime or repairs
- Reputational damage for manufacturers or businesses
Prevention and Mitigation
To prevent or mitigate similar failures in the future, several measures can be taken:
- Use high-quality materials with minimal defects
- Design components with adequate structural support and load capacity
- Conduct regular inspections and maintenance to identify potential failure surfaces early
- Implement stress analysis techniques to predict potential failure points
- Follow industry best practices and regulatory requirements for design and safety
Additional Considerations
Additional factors that may be relevant to the analysis of the failure surface include:
- Load history and operating conditions
- Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, or chemical exposure
- Ethical implications of failure, especially in critical applications
FAQ Resource
What is a failure surface?
A failure surface is a mathematical representation of the boundary beyond which a material or structure will fail under a given set of loading conditions.
How do you identify a failure surface?
The failure surface can be identified through experimental testing, numerical simulations, or analytical methods, depending on the complexity of the material or structure.
What are the consequences of failure?
Failure can lead to safety risks, property damage, economic losses, and reputational damage.